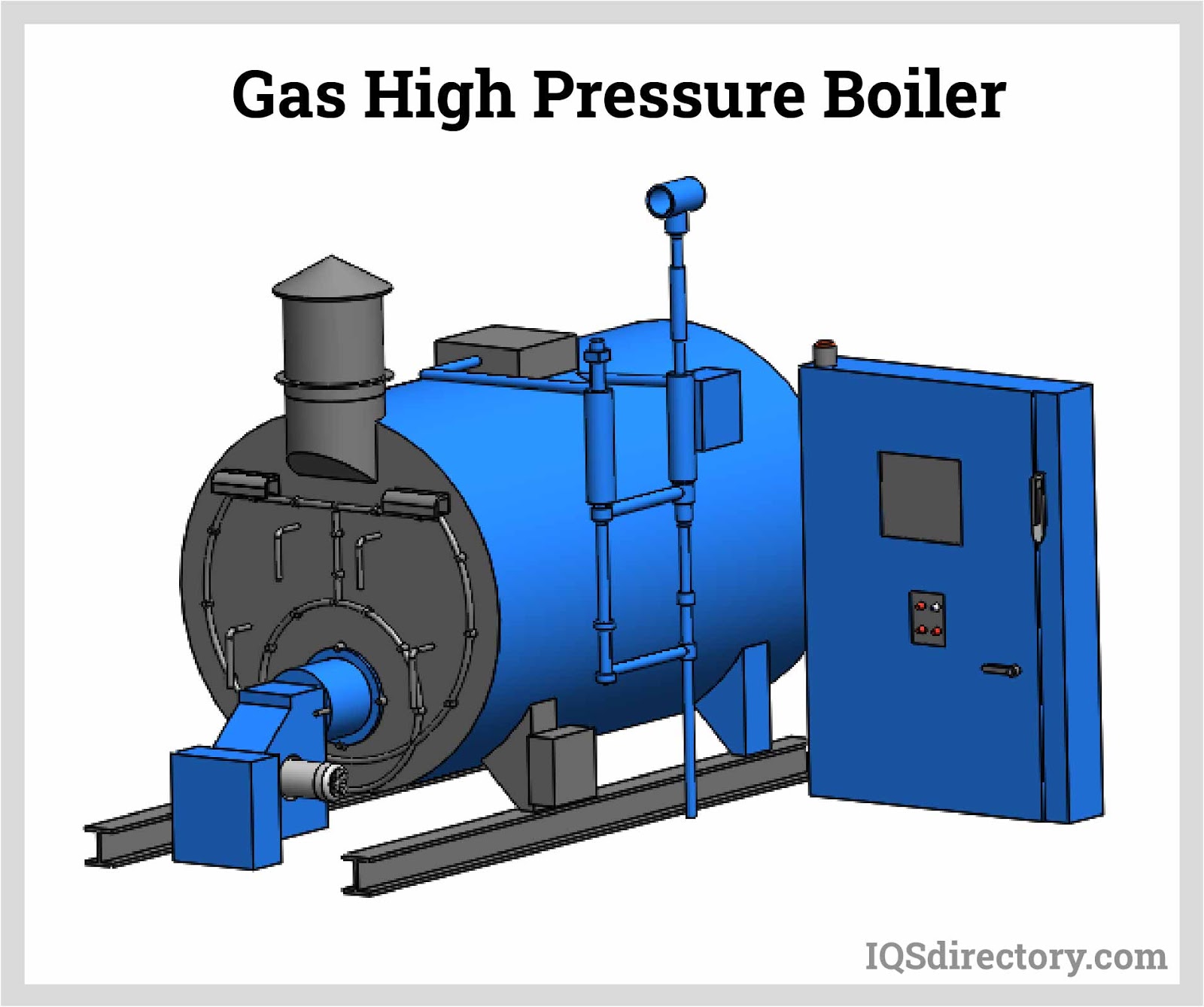
When a boiler operates with steam pressure greater than 80 bars, it is referred to as a high-pressure boiler above 80 bars. High pressure is widely used in power generation in thermal power plants. Read More…
We strive for the best at Unilux Advanced Manufacturing LLC. Our boilers are designed with superior materials. We are proud to say that we produced the world's first UL/FE boiler and our units provide the highest levels of safety and accountability.

As the inventor of the vertical tubeless boiler, Fulton has a reputation for success dating back to 1949. We`re a global manufacturer of steam, hot water and hydronic boilers, thermal fluid heaters, and custom engineered systems.

Miura Boiler Co., Ltd. has been manufacturing, designing, engineering and servicing gas, oil, coal, wood, solid waste, biomass & hybrid fuel-fired steam & gas and condensing since our inception. With installations across all industries worldwide, We are recognized for the highest code standards, innovative engineering and design, Energy Star rating, fully Integrated controls, and renewable,...
Indeck has the largest inventory of steam generating systems, a custom boiler design team and our own boiler manufacturing plant . Indeck is the complete steam power solution provider with emergency rental of 25,000 pph trailer-mounted rental boilers to the design of large custom million pound boilers. Our expertise includes watertube, mobile, packaged, waste heat, solid fuel, biomass and fire...
At California Boiler, we dedicate ourselves to delivering high-performance boiler solutions that meet the diverse needs of industries across the region. As a team, we design, supply, and support a full range of boiler systems, from standard hot water and steam units to specialized, high-capacity equipment tailored to unique applications.

At Burnham Commercial Boilers, we take pride in being a trusted name in the manufacturing and engineering of high-quality boilers designed to deliver dependable heating solutions for commercial and industrial applications. With decades of experience and innovation behind us, we focus on building equipment that meets the rigorous demands of facilities that require reliable performance, energy...

Nationwide Boiler is a leading supplier of new and reconditioned boilers for industrial facilities worldwide. We’re a manufacturer’s representative and stocking distributor for B&W package watertube boilers and Superior package firetube boilers, and we have fully reconditioned boilers in a variety of types and sizes. With sales, service and equipment depots throughout the U.S., we strive to...

More High Pressure Boiler Manufacturers
Classification of High-Pressure Boilers
High-pressure boilers are advanced industrial steam generating systems designed to operate at pressures significantly higher than conventional boilers, increasing thermal efficiency, output, and reliability. Modern high-pressure boilers play a crucial role in power generation, process heating, and critical industrial applications. To select the most suitable high-pressure boiler for your operation, it’s essential to understand the various categories and specialized types available in the market today.
Types of High-Pressure Boilers
- Lamont Boilers
- Benson Boilers
- Loeffler Boilers
- Schmidt-Hartmann Boilers
- Velox Boilers
- Super Critical Boilers
- Waste Heat Recovery Boilers
High-pressure boilers can also be categorized based on their mode of water circulation: natural circulation, forced circulation, and once-through boilers. Each design offers unique advantages for specific industrial use cases, including increased pressure handling, improved energy efficiency, and optimized steam generation. Below, we explore some of the most widely used high-pressure boiler types, their working principles, and their industrial significance.
Lamont Boilers
The Lamont boiler utilizes a forced circulation system, making it a preferred choice in industrial power plants requiring rapid steam generation and stable operation under fluctuating loads. Water enters the drum, is pumped to the evaporator section, and the resulting steam-water mixture returns to the drum. From there, steam is superheated and supplied to the prime mover. The forced circulation achieved through a circulation pump ensures high heat transfer rates and efficient evaporation per square foot of heating surface.
Compared to conventional water tube boilers, Lamont boilers offer several performance advantages: lighter design, enhanced safety, and the ability to achieve higher output with compact dimensions. The innovative forced circulation mechanism, operating at a pressure differential of approximately 2.5 bar, enables vaporized water flow rates 8 to 10 times greater than in natural circulation designs. This makes Lamont boilers a top choice in thermal power stations, marine propulsion systems, and process industries demanding high-pressure steam on demand.

Benson Boilers
The Benson boiler is a once-through, supercritical pressure boiler designed for optimized thermal efficiency and rapid startup. Invented by Marc Benson in Germany in 1923, Benson boilers are recognized for their compact design and ability to operate at extremely high pressures and temperatures. These boilers use small-diameter tubes (bore of about 25 mm) to form the furnace envelope, allowing feedwater to enter at the base and be heated to steam in a continuous spiral path.
One of the distinguishing features of Benson boilers is their recirculation capability under partial load conditions (below 60% MCR), which helps maintain steam quality and operational safety. A balancing header, positioned near the furnace top, compensates for variations in heat absorption across parallel spiral circuits. Once the steam-water mixture reaches the upper furnace sections, it undergoes superheating in pendant tube banks, ensuring high-quality steam output. Fossil fuel-fired Benson boilers also utilize flue gases for reheating, economizing, and air preheating, maximizing fuel-to-steam efficiency. These characteristics make Benson boilers an excellent solution for modern thermal power plants seeking supercritical or ultra-supercritical steam parameters.

Loeffler Boilers
Loeffler boilers are another advanced high-pressure boiler type, notable for their unique approach to steam generation. Rather than relying solely on water evaporation within tubes, Loeffler boilers use superheated steam from the boiler drum to evaporate the feedwater. This minimizes salt and scale deposition inside boiler tubes, making Loeffler boilers ideal in applications where water quality is inconsistent or where scale formation is a concern. They are commonly used in power plants requiring continuous, reliable operation and high steam purity.
Schmidt-Hartmann Boilers
The Schmidt-Hartmann boiler is a high-pressure, forced circulation boiler with a unique two-stage steam generation process. The system utilizes distilled water in a closed circuit, which is evaporated and then superheated. This steam then transfers its heat to an external water circuit via a heat exchanger. The design ensures excellent separation between working fluid and feedwater, making Schmidt-Hartmann boilers suitable for applications demanding very high purity steam, such as chemical processing and certain pharmaceutical sectors.
Velox Boilers
Velox boilers are high-pressure, forced circulation water-tube boilers that operate at exceptionally high rates of heat transfer. These boilers use a gas turbine-driven compressor to force air through the combustion chamber at supersonic velocities, resulting in rapid combustion and efficient heat exchange. Velox boilers are particularly suitable for applications requiring fast steam generation and compact design, such as combined heat and power (CHP) plants and peak demand power stations.
Super Critical Boilers
Supercritical and ultra-supercritical boilers push the limits of steam pressure and temperature, operating above the critical pressure of water (22.12 MPa). In these boilers, there is no distinction between water and steam, enabling the generation of steam at extremely high thermal efficiency and minimal fuel consumption. Supercritical boilers are the backbone of modern utility power plants, contributing to reduced emissions and improved environmental performance by maximizing plant efficiency.
Waste Heat Recovery Boilers
Waste heat recovery boilers are engineered to capture and convert waste heat from industrial processes, exhaust gases, and incinerators into usable thermal energy. These boilers contribute significantly to energy savings, improved process efficiency, and lower environmental impact. Waste heat sources include steel mills, non-ferrous metal plants, chemical production facilities, cement manufacturing, and other heavy industries.
By recovering and reusing process heat, waste heat recovery boilers reduce fuel costs, decrease greenhouse gas emissions, and help businesses meet stringent energy efficiency and sustainability targets. They are often integrated into cogeneration systems, district heating networks, and process steam supplies, making them an essential element of modern industrial energy management strategies.

Working Principle of High-Pressure Boilers
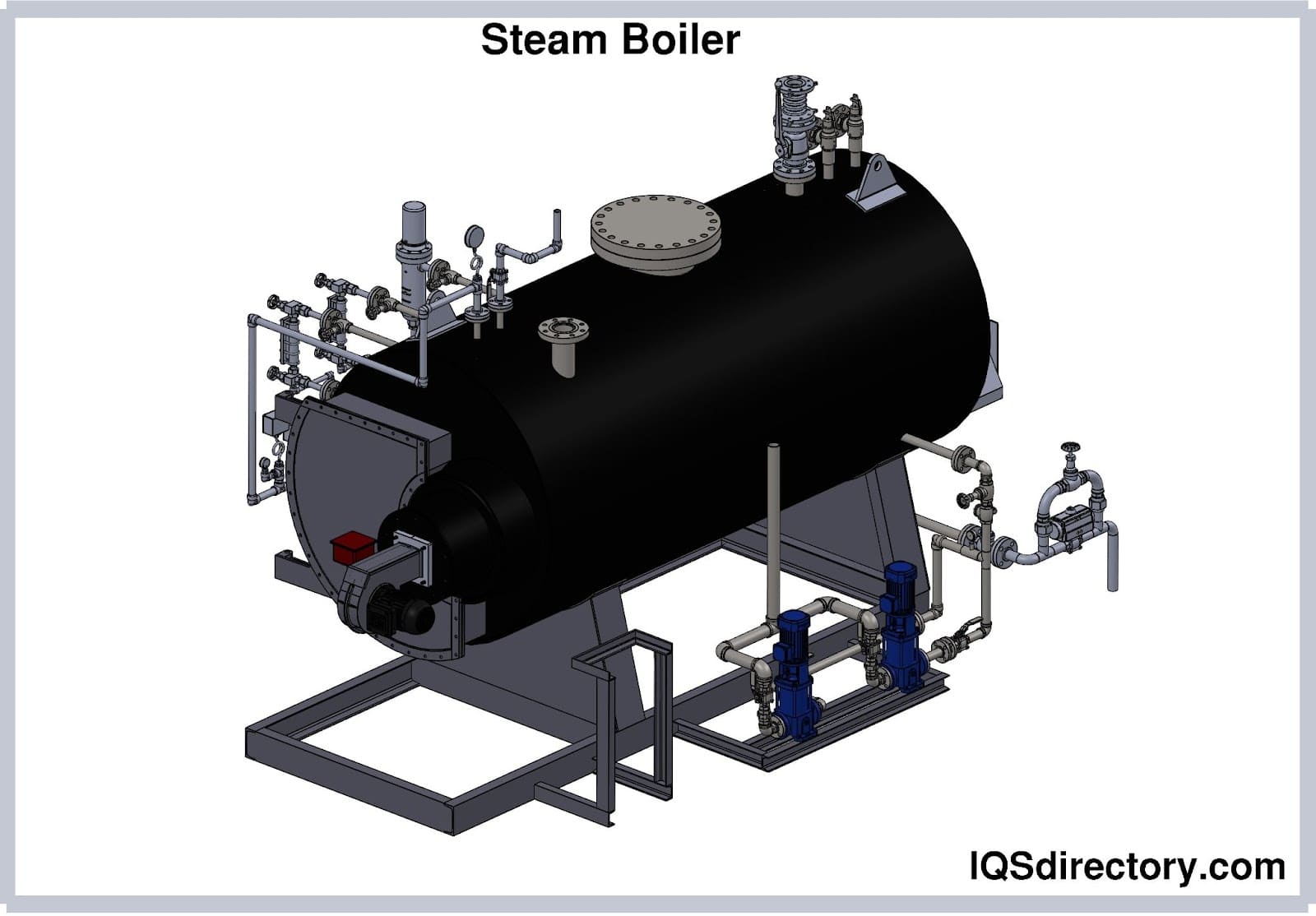
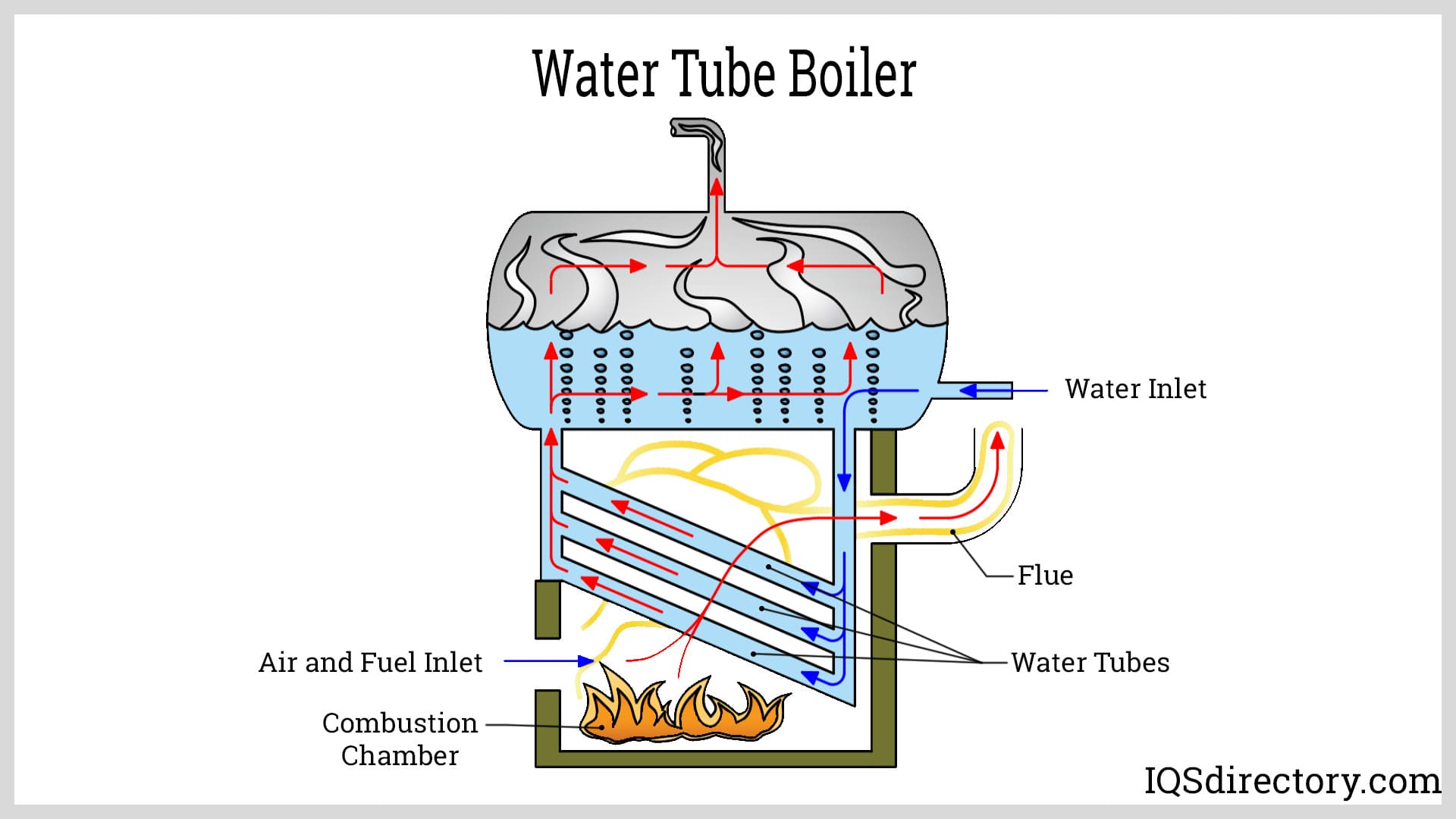
High-pressure boilers operate on the principle of circulating water through a series of tubes where it is heated by contact with hot combustion gases. Water cycles repeatedly from the shell (water drum) to the water tubes and back to the shell before being converted to high-pressure steam. As water circulates within the tubes, it absorbs heat transferred indirectly through tube walls from flue gases, gradually transforming into steam.
The circulation ratio—the ratio of water circulated to the amount of steam generated—is a crucial design consideration for high-pressure water tube boilers. Two primary circulation methods are used:
- Natural Circulation: Water circulates spontaneously due to density differences created by temperature gradients between hot and cold water. This method is common in older or smaller high-pressure boilers but requires careful design to avoid issues like tube overheating or thermal stress.
- Forced Circulation: A secondary pump (in addition to the feedwater pump) actively forces water through the tubes, ensuring consistent flow and eliminating the risk of localized overheating. Forced circulation is widely used in modern high-pressure boilers, especially in large-scale power plants and critical industrial applications where operational safety and efficiency are paramount.
Some high-pressure boiler designs, such as the water tube boilers used in power generation and petrochemical processes, feature once-through operation. In these systems, water passes through the boiler only once, converting entirely to steam without recirculation—ideal for supercritical and ultra-supercritical applications where rapid response and high efficiency are required.
Applications of High-Pressure Boilers
High-pressure boilers are integral to a wide range of industrial and commercial sectors. Their ability to generate high-pressure, high-temperature steam makes them suitable for the following applications:
- Power Generation: High-pressure steam produced in boilers is expanded in steam turbines or engines to generate mechanical or electrical power. These systems form the backbone of thermal power stations, combined cycle plants, and cogeneration facilities.
- Heating Systems: In cold climates and large-scale infrastructure, high-pressure boilers supply steam or hot water for district heating networks, commercial building heat, and domestic hot water production.
- Industrial Processes: Sectors such as sugar, cement, agriculture, textiles, paper, food processing, and chemicals utilize high-pressure steam for a myriad of industrial processes—including sterilization, pasteurization, drying, sizing, and bleaching.
- Petrochemical & Refining: High-pressure boilers provide process steam for cracking, reforming, and other refinery operations, ensuring reliable, continuous plant operation and energy integration.
- Marine & Locomotive: Modern ships and locomotives use compact high-pressure boilers for propulsion and auxiliary power, benefiting from rapid startup and high energy density.
- Waste Heat Recovery: Industrial facilities employ waste heat recovery boilers to convert otherwise lost heat into productive energy, supporting sustainability initiatives and reducing operational costs.
Considering investing in a high-pressure boiler system? Ask yourself: What is the primary purpose of the steam—power generation, heating, or process applications? What are your pressure and capacity requirements? Are energy efficiency and emissions reduction priorities for your facility? Addressing these questions will help you identify the ideal boiler technology for your business needs.
Advantages of High-Pressure Boilers
High-pressure boilers offer several compelling benefits over traditional low-pressure steam generators, making them a preferred choice for modern industrial operations:
- The use of numerous small-diameter tubes maximizes the heat transfer area, making optimal use of combustion heat and improving overall thermal efficiency.
- Powertherm and similar high-pressure boilers feature a parallel set of tubes, minimizing flow resistance and ensuring uniform water distribution—critical for safe, reliable operation.
- The horizontal arrangement of steam boiler components enhances accessibility, simplifies maintenance, and promotes comfortable operation for technical staff.
- Uniform heating of boiler elements reduces thermal stress, lowering the risk of warping or cracking and extending equipment lifespan.
- Rapid water flow through tubes prevents scale formation, a common cause of efficiency loss and tube failure in conventional boilers.
- High-pressure boilers are versatile, capable of operating efficiently with a variety of fuels, including natural gas, oil, coal, and alternative energy sources—supporting fuel flexibility and security of supply.
- The ability to generate high-quality steam at elevated pressures enables integration with advanced steam turbines, combined cycle plants, and cogeneration systems, further improving energy utilization and plant performance.
Disadvantages of High-Pressure Boilers
While high-pressure boilers deliver substantial performance and economic benefits, some challenges and drawbacks should be considered during system selection and operation:
- Insufficient water flow through tubes can lead to localized overheating, potentially resulting in tube rupture or system failure.
- Bubble formation on tube surfaces (nucleate boiling) may impede heat transfer, reducing efficiency and increasing the risk of thermal stress.
- High-pressure boiler systems require advanced controls, regular maintenance, and skilled operators to ensure safe, reliable performance—adding to operational complexity and cost.
- The initial investment in high-pressure boiler technology is typically higher than for low-pressure alternatives, though this is often offset by improved efficiency and lower long-term fuel costs.
- Water treatment and quality management are critical to prevent scale, corrosion, and fouling in high-pressure systems, necessitating robust monitoring and treatment programs.
Buyer’s Guide: Choosing the Right High-Pressure Boilers Manufacturer
Selecting the optimal high-pressure boiler manufacturer is a critical decision that affects your facility’s energy efficiency, operational reliability, and compliance with environmental regulations. To ensure the best outcome when purchasing high-pressure boilers, it’s wise to conduct a thorough comparison of top manufacturers and suppliers.
- Compare Multiple Suppliers: Evaluate at least five high-pressure boiler manufacturers using our curated list. Look for companies with proven expertise, a strong track record, and technical capabilities aligned with your project requirements.
- Review Business Profiles: Each manufacturer’s profile provides insights into their specialization, certifications, engineering support, and after-sales service. This information helps narrow down options based on your industry, application, and budget.
- Request Detailed Quotes: Use our convenient RFQ (Request for Quote) form to send inquiries to multiple suppliers simultaneously. Be clear about your pressure, capacity, fuel type, and regulatory compliance needs.
- Assess Technical Support: Ongoing technical assistance, spare parts availability, and training services are essential for long-term performance and minimal downtime.
- Preview Company Websites: Take advantage of our patented website previewer to explore each manufacturer’s offerings, case studies, and project references. This helps you identify partners with experience in your sector.
Not sure how to choose the best high-pressure boiler for your process? Ask the experts:
- What are the key differences between natural circulation, forced circulation, and once-through boiler designs?
- How do fuel options, emissions regulations, and energy efficiency targets affect boiler selection?
- What are the maintenance and lifecycle cost considerations for high-pressure steam systems?
- Are there turnkey solutions or custom engineering services available for your industry?
Our team is here to support your research and procurement journey—contact us for in-depth consulting or a personalized quote.
Frequently Asked Questions About High-Pressure Boilers
What is considered a high-pressure boiler?
A high-pressure boiler is a steam-generating device that operates at pressures above 15 psi (pounds per square inch) or 1 bar, with modern industrial boilers commonly exceeding 100 bar (1450 psi). These systems are engineered to produce large volumes of steam at elevated pressures and temperatures, making them essential for power generation, process heating, and heavy industry.
What industries use high-pressure boilers?
High-pressure boilers are used extensively in electric power generation, petrochemical refining, food and beverage processing, textile manufacturing, pulp and paper production, pharmaceutical plants, district heating systems, and marine propulsion. Their ability to deliver reliable, high-quality steam supports a broad range of critical industrial operations.
How do I maintain a high-pressure boiler?
Routine maintenance of high-pressure boilers includes regular inspection of tubes and drums, monitoring of water chemistry, cleaning of heat transfer surfaces, calibration of safety valves and controls, and periodic testing of emergency shutdown systems. Implementing a comprehensive preventive maintenance plan helps prevent breakdowns, extend boiler life, and ensure compliance with safety standards.
Can high-pressure boilers be customized for specific applications?
Yes, leading manufacturers offer custom-engineered high-pressure boiler solutions tailored to unique process requirements, spatial constraints, and regulatory demands. Options include modular skid-mounted systems, integrated control panels, advanced emissions reduction technologies, and compatibility with diverse fuel sources.
What are the main factors to consider when buying a high-pressure boiler?
- Required steam pressure and capacity
- Fuel type and availability
- Thermal efficiency and emissions performance
- Water quality and treatment requirements
- Installation space and site constraints
- Compliance with industry standards and regulations (e.g., ASME, ISO, local codes)
- Manufacturer’s technical support and warranty
Start Your High-Pressure Boiler Project Today
Ready to take the next step? Whether you are upgrading an aging steam system, building a new power plant, or seeking energy-saving waste heat recovery solutions, our network of leading high-pressure boiler manufacturers and suppliers can help you achieve your goals. Use our advanced search tools to filter suppliers by location, product specialization, and certifications. Request a quote or schedule a technical consultation today to find the right high-pressure boiler for your facility’s needs.
Want to learn more about the latest trends in industrial boiler technology, safety standards, or energy efficiency upgrades? Explore our in-depth guides, case studies, and expert insights—or ask a question using our online contact form. We’re committed to helping you maximize productivity, safety, and sustainability with state-of-the-art high-pressure steam solutions.






 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services