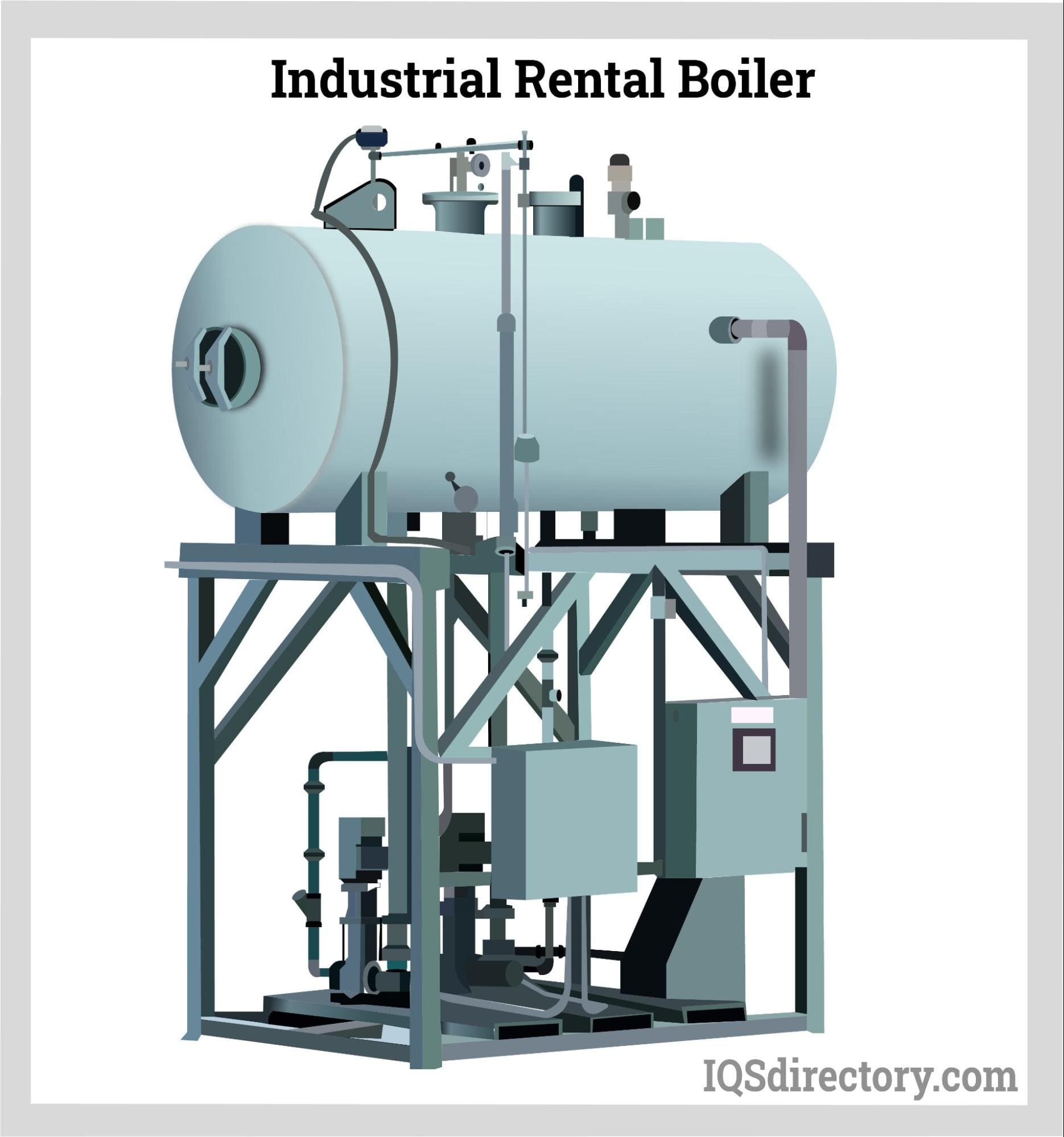
Industrial boilers are closed vessels that use an external fuel source to heat water or another liquid held within and transform these liquids into a larger source of energy. This energy results from the increased pressure water endures while heated in a confined space. Read More…
We strive for the best at Unilux Advanced Manufacturing LLC. Our boilers are designed with superior materials. We are proud to say that we produced the world's first UL/FE boiler and our units provide the highest levels of safety and accountability.

As the inventor of the vertical tubeless boiler, Fulton has a reputation for success dating back to 1949. We`re a global manufacturer of steam, hot water and hydronic boilers, thermal fluid heaters, and custom engineered systems.

Miura Boiler Co., Ltd. has been manufacturing, designing, engineering and servicing gas, oil, coal, wood, solid waste, biomass & hybrid fuel-fired steam & gas and condensing since our inception. With installations across all industries worldwide, We are recognized for the highest code standards, innovative engineering and design, Energy Star rating, fully Integrated controls, and renewable,...
Indeck has the largest inventory of steam generating systems, a custom boiler design team and our own boiler manufacturing plant . Indeck is the complete steam power solution provider with emergency rental of 25,000 pph trailer-mounted rental boilers to the design of large custom million pound boilers. Our expertise includes watertube, mobile, packaged, waste heat, solid fuel, biomass and fire...
At California Boiler, we dedicate ourselves to delivering high-performance boiler solutions that meet the diverse needs of industries across the region. As a team, we design, supply, and support a full range of boiler systems, from standard hot water and steam units to specialized, high-capacity equipment tailored to unique applications.

At Burnham Commercial Boilers, we take pride in being a trusted name in the manufacturing and engineering of high-quality boilers designed to deliver dependable heating solutions for commercial and industrial applications. With decades of experience and innovation behind us, we focus on building equipment that meets the rigorous demands of facilities that require reliable performance, energy...

Nationwide Boiler is a leading supplier of new and reconditioned boilers for industrial facilities worldwide. We’re a manufacturer’s representative and stocking distributor for B&W package watertube boilers and Superior package firetube boilers, and we have fully reconditioned boilers in a variety of types and sizes. With sales, service and equipment depots throughout the U.S., we strive to...

More Industrial Boiler Manufacturers
Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Boilers: Types, Components, Applications, and Selection Tips
Industrial boilers are critical pieces of process equipment that provide heat, steam, or hot water for a wide range of commercial and industrial applications. Whether you’re searching for reliable steam generation systems for manufacturing or efficient hot water boilers for building heating, understanding the fundamentals of industrial boilers will help you make informed decisions for your facility. This guide covers key types of industrial boilers, their core components, fuel options, industrial use cases, and essential factors to consider when selecting a boiler manufacturer or supplier.

What Are Industrial Boilers?
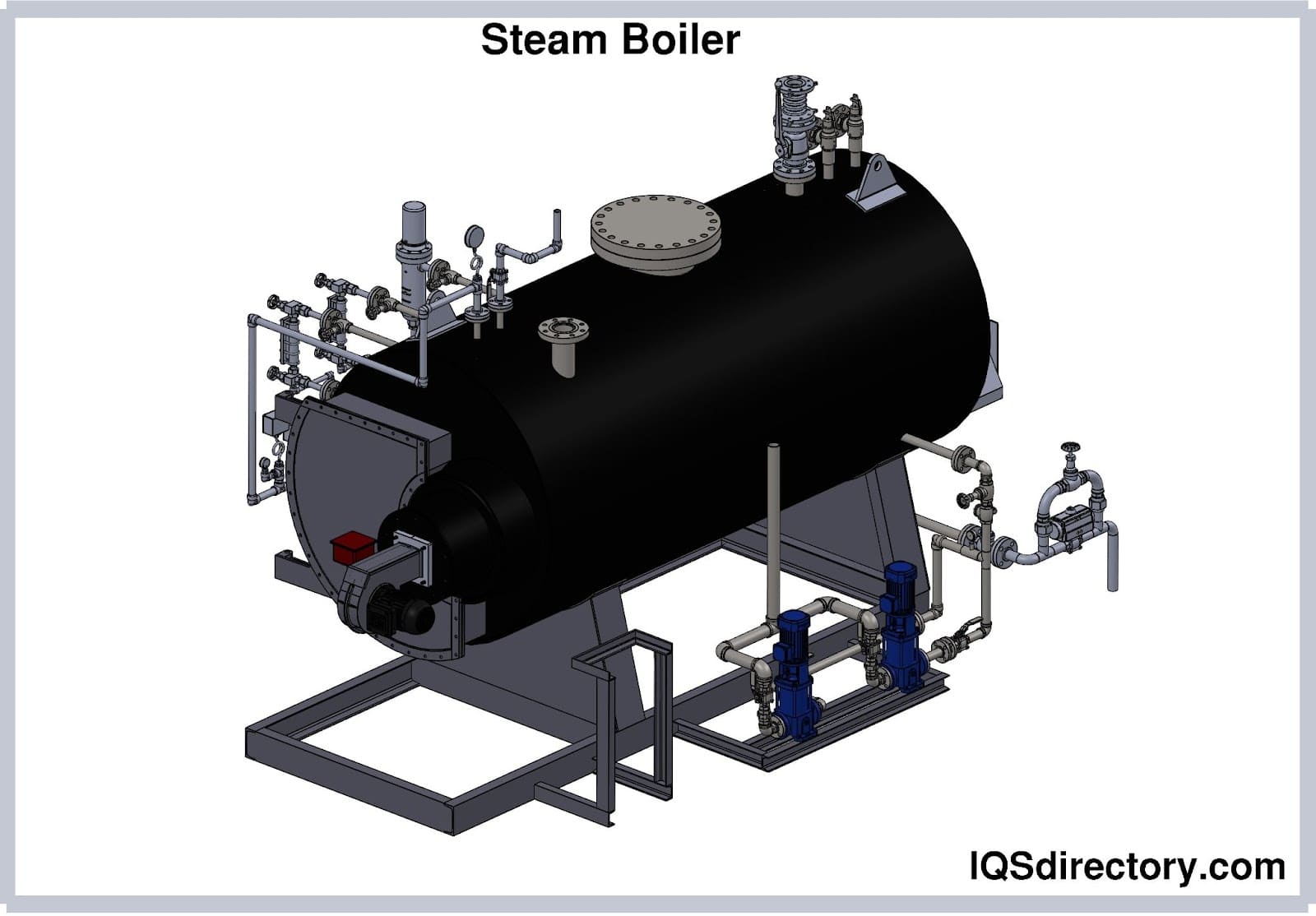
Industrial boilers are closed vessels designed to convert water into steam or hot water by applying heat energy. These heavy-duty systems are indispensable in various sectors such as manufacturing, food processing, chemical production, power generation, healthcare, and agriculture. The two primary categories of industrial boilers are steam boilers and hot water boilers:
- Steam Boilers: Heat water to produce pressurized steam, which is distributed via piping to drive turbines, power machinery, or support industrial processes.
- Hot Water Boilers: Circulate heated water through a system of pumps and pipes for space heating, sanitation, or process requirements.
Both types of boilers offer cost-effective, scalable, and reliable heating solutions across a broad spectrum of industries, supporting everything from building comfort to high-volume industrial processes.
Key Components of Industrial Boilers
Modern industrial boilers are engineered for efficiency, safety, and durability. They consist of several critical components that work together to generate and distribute heat or steam. If you’re evaluating boiler designs, consider these essential parts:
- The Burner: Initiates the combustion process by igniting fuel (such as natural gas, oil, coal, or electricity) to create heat. Advanced burners offer precise fuel-air mixing for maximum efficiency and low emissions.
- Combustion Chamber: Constructed from robust steel or cast iron, the combustion chamber contains the burning fuel and withstands extreme temperatures. Effective insulation minimizes energy loss and enhances boiler safety.
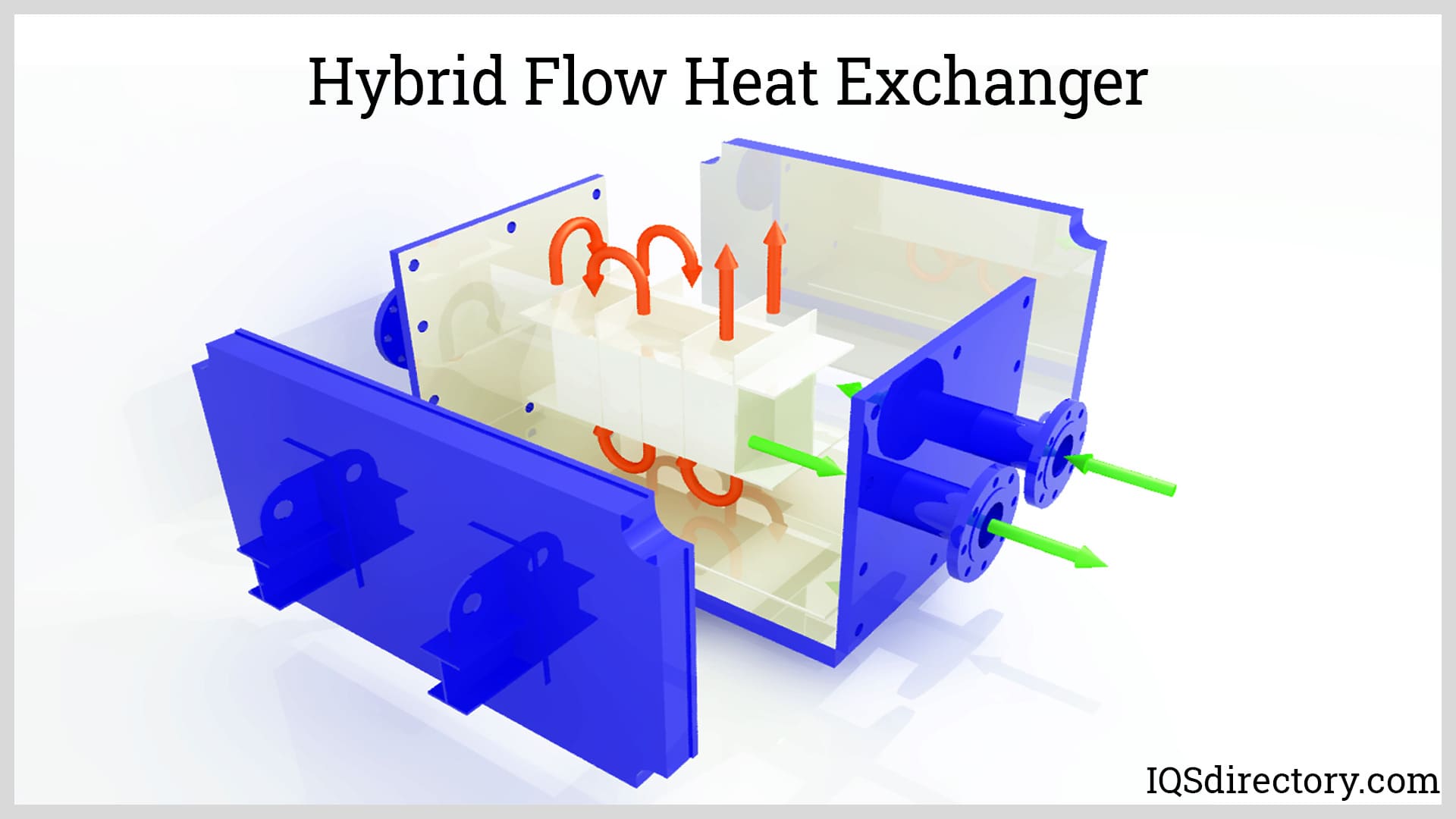
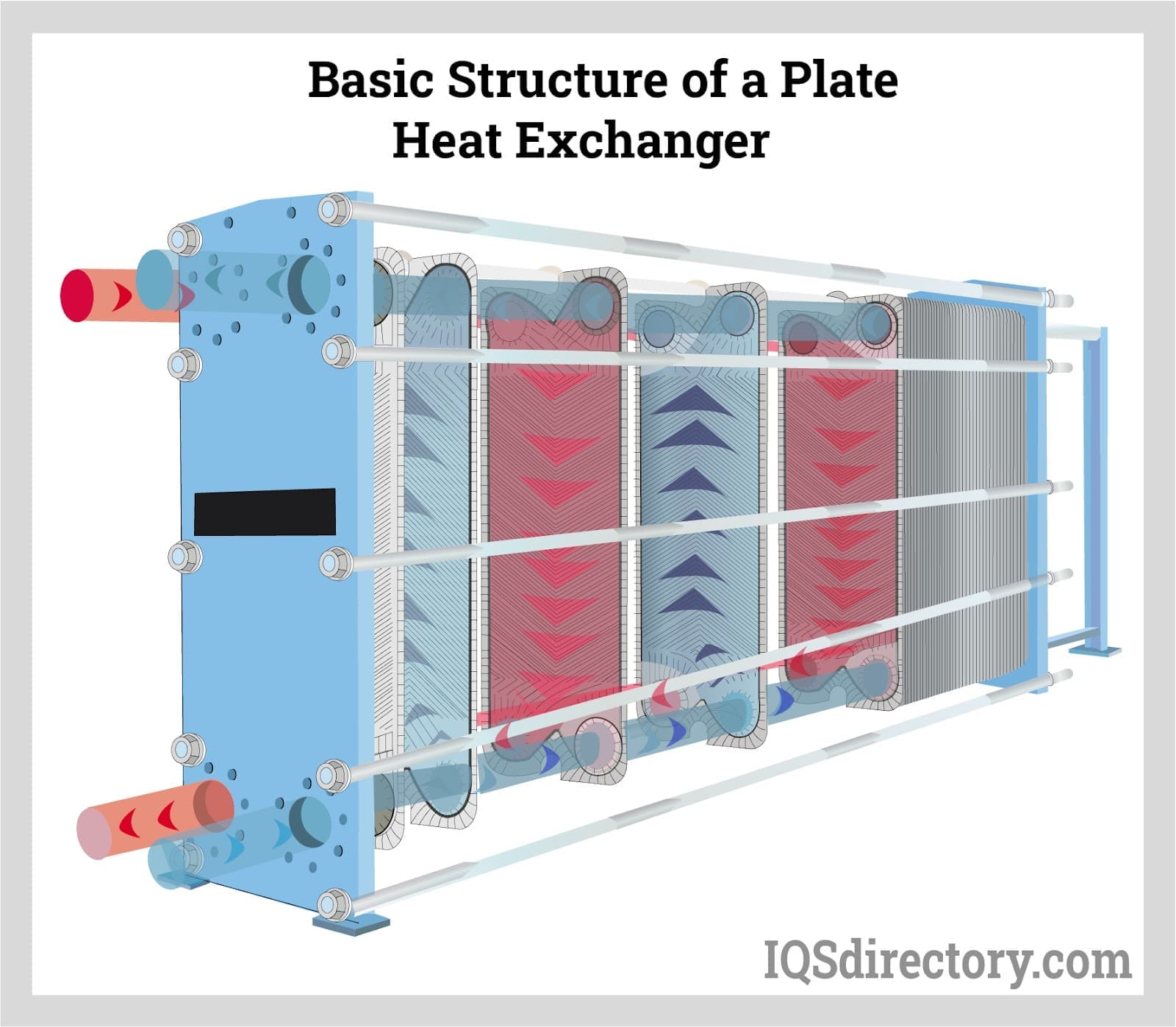
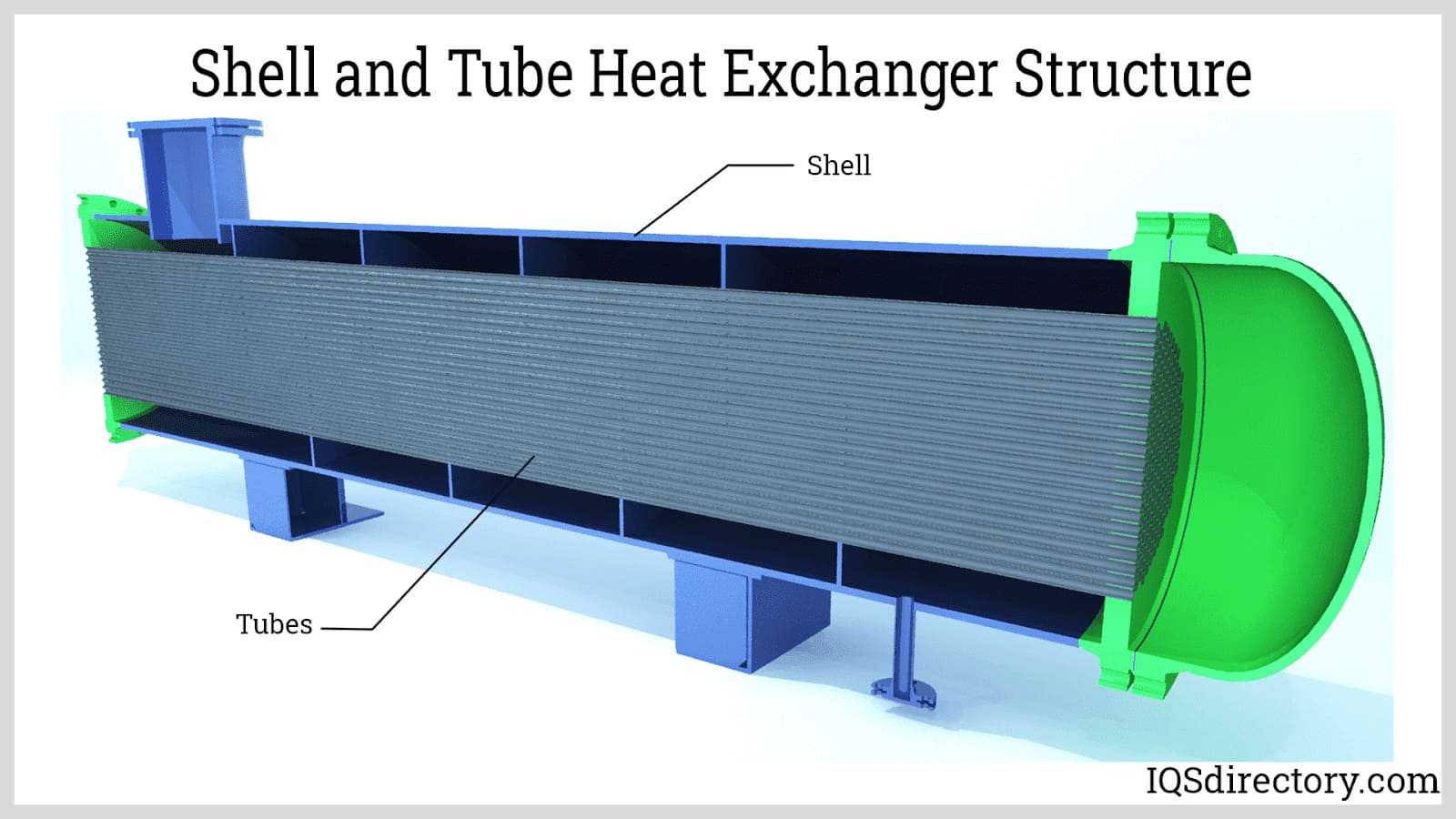
- Heat Exchanger: Transfers the heat generated in the combustion chamber to water or steam, often via tubes or coils. High-efficiency heat exchangers are vital for reducing fuel consumption and operational costs.
- Supply and Return Lines: Direct the flow of water, steam, or condensate throughout the facility, ensuring seamless integration with process equipment, radiators, or heating systems.
- Pumps: Circulate water or steam through the system. Proper pump selection is crucial for maintaining pressure, flow rate, and system reliability.
- Control Mechanisms: Automated controls manage temperature, pressure, safety shutoffs, and fuel supply, enabling remote monitoring and optimizing operational efficiency.
- Steam Drum & Mud Drum: In larger steam boilers, the steam drum collects generated steam, while the mud drum gathers sediment and solid byproducts for periodic removal, helping maintain system cleanliness and efficiency.
Do you want to learn more about boiler components and how they impact performance? Contact our experts for detailed technical insights.
Industrial Boiler Fuel Sources
Boilers can be powered by a variety of fuels, each with unique advantages and considerations for cost, availability, environmental impact, and regulatory compliance. Common energy sources for industrial boilers include:
- Natural Gas: Clean-burning, widely available, and efficient. Ideal for facilities prioritizing low emissions and operational flexibility.
- Fuel Oil (Diesel, Heavy Oil): Suitable for locations where natural gas is unavailable. Offers high energy density but may involve higher emissions and maintenance.
- Electricity: Electric boilers are eco-friendly and produce zero onsite emissions, making them suitable for cleanrooms and green building projects.
- Coal: Traditional but declining due to environmental regulations. Still used in some large-scale power and industrial facilities.
- Biomass and Alternative Fuels: Renewable options such as wood chips, pellets, or agricultural waste can lower carbon footprint.
- Propane: Popular in rural or off-grid settings as a substitute for natural gas.
Choosing the right fuel type involves balancing cost, environmental goals, and infrastructure compatibility. Want a fuel cost comparison or emissions analysis? Request a consultation.
Types of Industrial Boilers
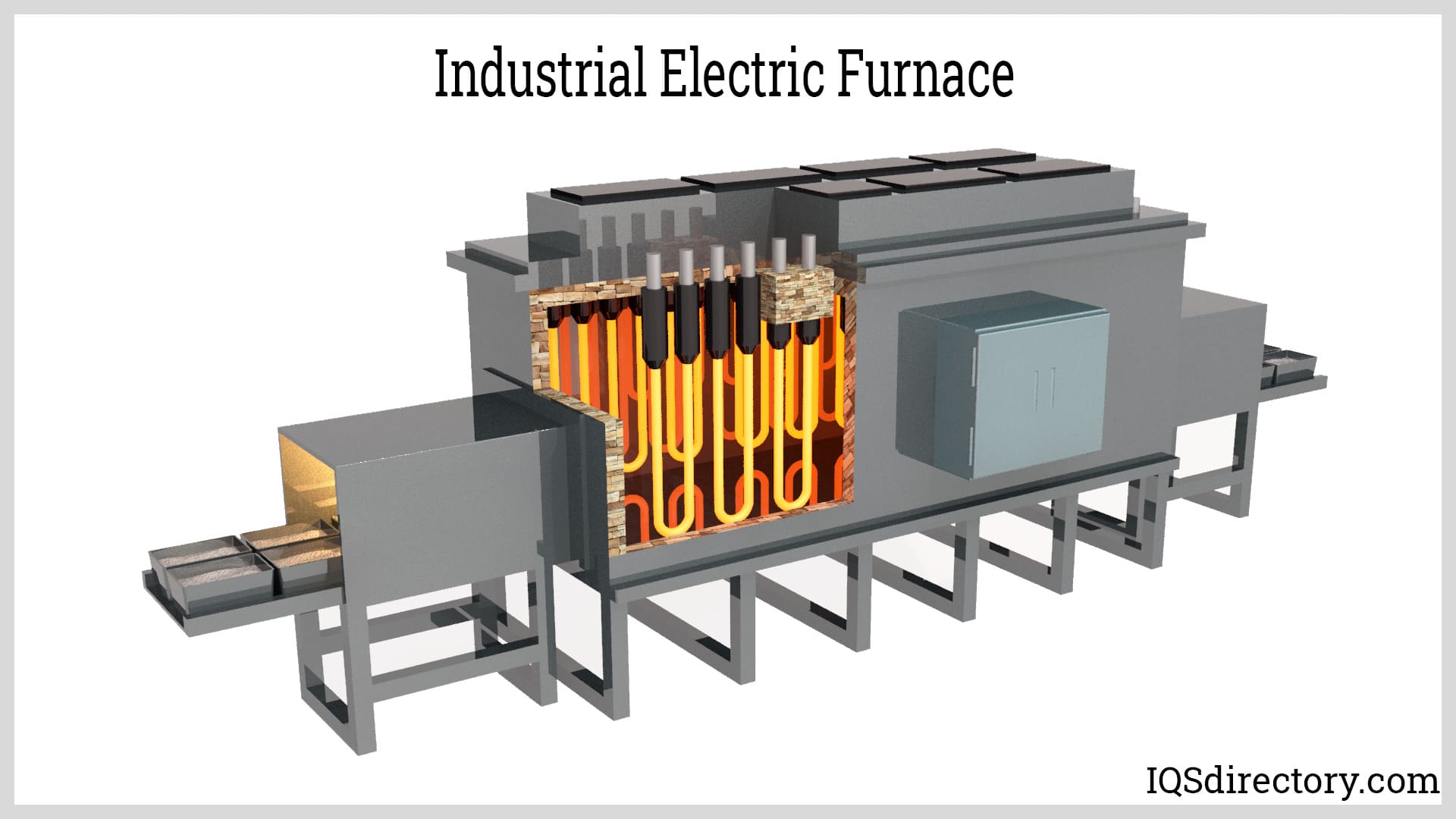
Electric Boilers
Electric boilers are increasingly popular due to their simplicity, safety, and eco-friendly operation. Instead of burning fossil fuels, they use electric resistance heating elements to convert electrical energy into heat. Key benefits of electric boilers include:
- Zero onsite emissions—ideal for facilities with strict air quality regulations or sustainability goals.
- Lower installation and maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts and simpler design.
- Compact footprint and quiet operation—perfect for urban locations or noise-sensitive environments.
- Easy integration with renewable power sources such as solar or wind energy.
However, electric boilers can have higher operational costs in regions with expensive electricity rates. They are best suited for small to medium-scale applications, backup heating, or facilities where clean energy is a top priority.

Fire Tube Boilers
Fire tube boilers are classic designs in which hot combustion gases pass through tubes surrounded by water. This configuration is common among small to medium-sized businesses seeking straightforward, factory-assembled (“packaged”) solutions. Advantages of fire tube boilers include:
- Relatively easy installation—most systems arrive preassembled with pumps, controls, and safety devices.
- Consistent performance for low- to medium-pressure steam (up to 2000 boiler horsepower).
- Lower up-front costs compared to some custom-built boiler systems.
However, fire tube boilers have limitations in terms of steam output and efficiency at high pressures. They carry a greater risk of explosion if not properly maintained. For businesses with intermittent or modest steam demands, fire tube boilers deliver reliable service and quick startup times.

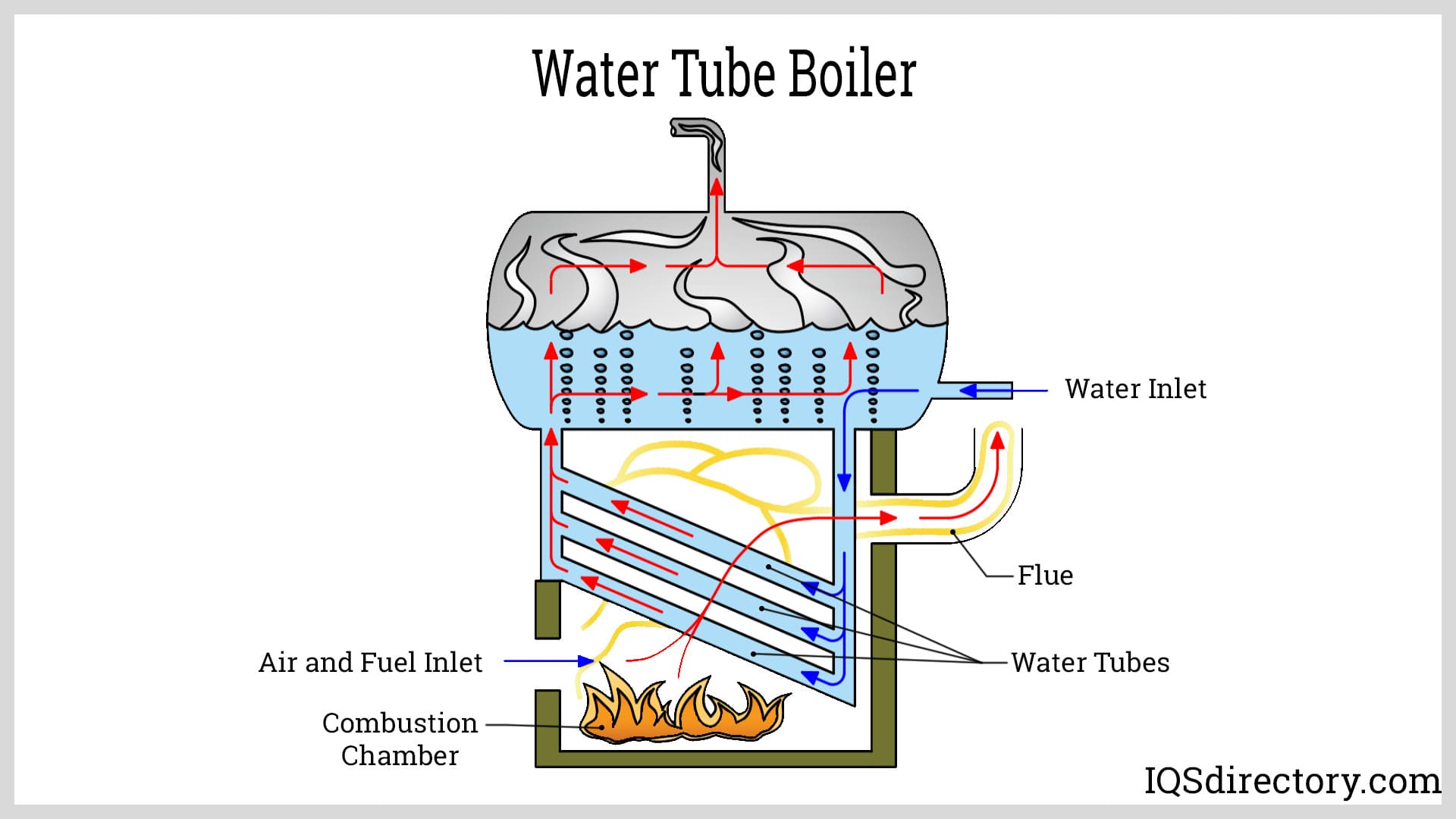
Water Tube Boilers
Water tube boilers feature a distinct design in which water circulates inside tubes that are surrounded by hot combustion gases. This arrangement enables higher pressures, greater steam capacity, and improved fuel efficiency compared to fire tube models. Notable advantages include:
- Superior energy efficiency—minimal fuel waste and optimized heat transfer.
- High-pressure steam output, ideal for power plants, chemical manufacturing, or large-scale food processing facilities.
- Customizability—often engineered to match specific site requirements or process needs.
- Enhanced safety—reduced risk of catastrophic failure due to lower water volume at high pressures.
Water tube boilers are typically built on-site, allowing for larger capacities and integration with complex industrial systems. They require skilled operation and regular maintenance but offer unmatched performance for demanding applications.

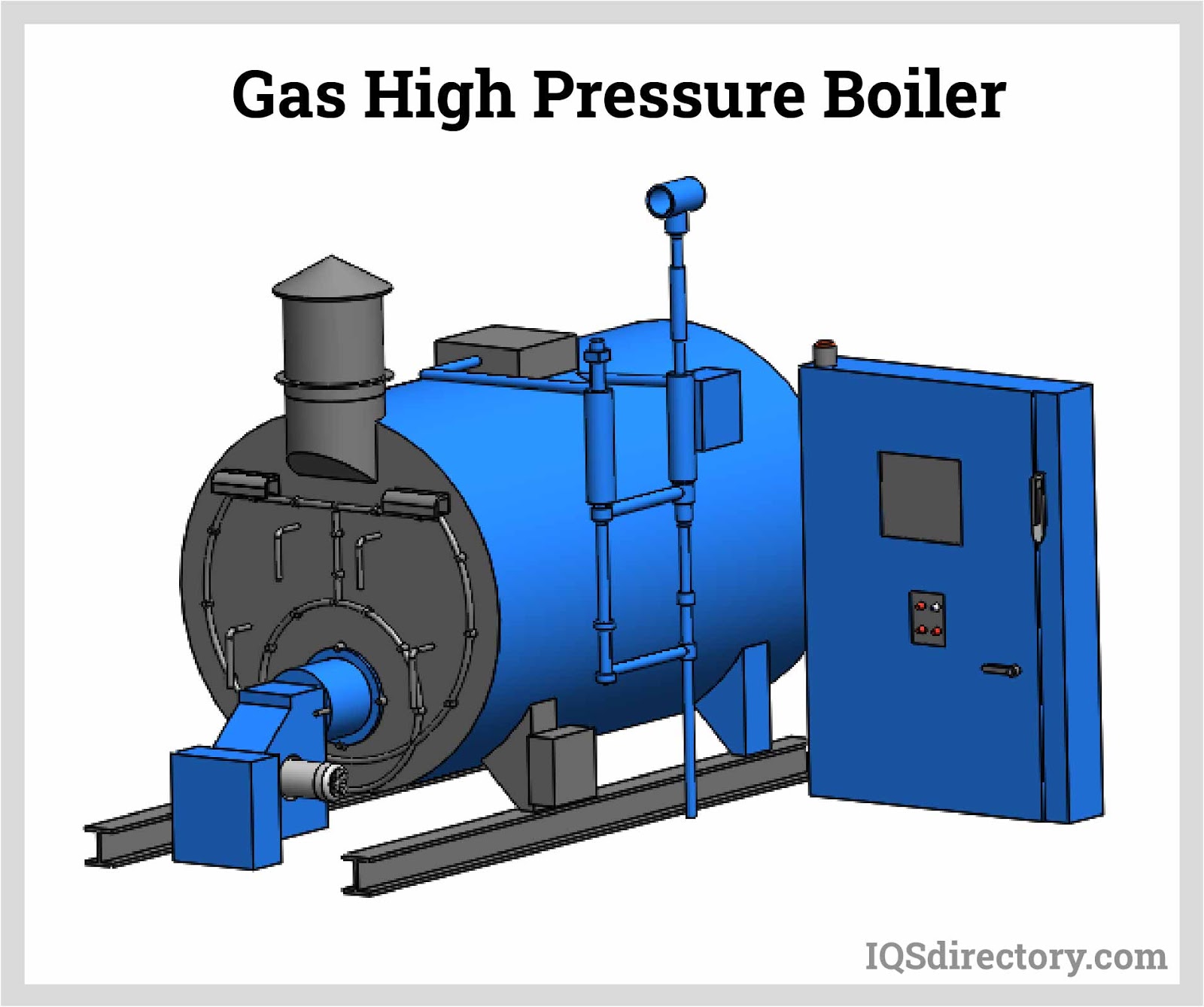
Natural Gas Boilers
Natural gas boilers are a leading choice for modern industry. They burn cleanly, produce minimal emissions, and are compatible with advanced control systems for precise temperature and pressure regulation. Key features of gas-fired boilers:
- Fast response time and excellent load-following capability for dynamic process environments.
- Lower lifecycle costs thanks to high fuel efficiency and reduced maintenance needs.
- Propane gas can be used as an alternative in rural areas without natural gas pipelines, providing flexibility and continuity of operations.
Interested in comparing natural gas boilers to alternative fuel systems? Start your comparison here.
Oil-Fired Boilers
Oil boilers use diesel, light oil, or heavy oil as their primary fuel source. They are common in facilities where gas infrastructure is unavailable or unreliable. Benefits and considerations include:
- Robust performance and high output—efficiency ratings can reach up to 86% or more.
- Ability to operate in remote locations or during fuel supply disruptions.
- Potential for dual-fuel operation, allowing seamless switching between oil and gas depending on cost or availability.
Oil-fired boilers require regular burner maintenance and fuel storage management. They may have higher emissions than natural gas systems, but advancements in burner technology are improving their environmental footprint.

Condensing Boilers
Condensing boilers are at the forefront of energy efficiency. These systems extract additional heat from exhaust gases by condensing water vapor, achieving thermal efficiencies of 90% or higher. Noteworthy advantages:
- Substantial fuel savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions—ideal for organizations with sustainability mandates.
- Lower operating costs due to heat recovery and minimized fuel waste.
- Most condensing boilers are powered by natural gas, but designs exist for oil or propane as well.
Condensing technology is especially attractive for new construction, retrofits, and facilities seeking the best lifecycle value.
Additional Types and Specialized Industrial Boilers
- Biomass Boilers: Utilize renewable organic materials for fuel, helping facilities meet renewable energy goals and reduce carbon emissions.
- Modular Boilers: Consist of multiple small units that can be combined for scalability and redundancy—ideal for variable process loads.
- Waste Heat Recovery Boilers: Capture heat from industrial exhaust streams to provide free energy for process or building needs.
Curious about which type of boiler best matches your process, budget, and sustainability targets? Request expert guidance.
Industrial Boiler Applications: Where and How Are They Used?
Industrial boilers are foundational to the operation of countless sectors. Explore some of the most common industries and applications below:
Agriculture
Boilers support agricultural operations by providing hot water and steam for greenhouse heating, animal husbandry, crop processing, and equipment sterilization. Steam-based soil sterilization is a proven method for controlling weeds, pathogens, and pests, thereby improving crop yields and soil health. Steam sterilization also releases beneficial nutrients from organic matter, although it does not affect heat-resistant spore-forming bacteria.
- Greenhouse climate control and humidity management
- Sanitization of animal pens, milking equipment, and processing tools
- Crop drying, distillation, and food processing
Healthcare and Hospitals
In healthcare environments, industrial boilers play an essential role in sterilizing surgical instruments, maintaining clean and safe environments, providing space heating, and supporting hot water needs for kitchens and laundry facilities. Reliable steam generation is critical for infection control and patient safety.
- Sterilization of surgical suites and medical devices
- Heating and hot water supply for patient rooms, labs, and clinics
- Laundry and dietary department sanitation
Manufacturing and Processing Industries
Manufacturing relies on industrial boilers for process heating, steam-driven power, and material transformation. Common applications include:
- Food and beverage production (pasteurization, cooking, and cleaning)
- Chemical and pharmaceutical processing (reaction heating, distillation, sterilization)
- Pulp and paper mills (digestion, bleaching, drying)
- Textile production (dyeing, finishing, drying)
- Automotive and metalworking (parts cleaning, surface preparation, heat treatment)
Power Generation
Power plants use high-capacity, high-pressure boilers to generate steam that drives turbines for electricity production. These systems demand robust construction, advanced controls, and high efficiency to meet continuous load demands and regulatory standards.
Commercial Buildings and District Heating
Large commercial complexes, schools, universities, and district energy systems use industrial boilers for centralized heating and hot water distribution. Centralized boiler plants offer improved energy management, redundancy, and cost savings for multi-building campuses.
Other Applications
Industrial boilers are also found in refineries, breweries, laundries, hotels, and any facility requiring high-volume hot water or steam. Their applications extend to power generation, manufacturing, and specialized environments such as cleanrooms or pharmaceutical labs.
Looking for a solution tailored to your specific application? Connect with our engineering team.
Benefits of Modern Industrial Boilers
- High efficiency and energy savings reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
- Advanced safety features protect personnel and equipment from overpressure or combustion hazards.
- Automated controls and remote monitoring improve reliability, diagnostics, and ease of operation.
- Flexible fuel options accommodate changing market conditions and supply chains.
- Modular and scalable designs enable phased expansions and resilience against equipment failures.
How to Choose the Right Industrial Boiler
Selecting the optimal industrial boiler requires careful evaluation of your facility’s thermal needs, budget, fuel availability, regulatory requirements, and long-term operational goals. Here are the key decision factors to consider:
- Capacity and Output: Assess your peak and average steam or hot water demand. Oversizing wastes energy, while undersizing limits productivity.
- Fuel Type and Cost: Evaluate fuel availability, price volatility, and infrastructure compatibility.
- Efficiency and Emissions: Look for high-efficiency designs and low-emission burners to meet environmental standards and qualify for incentives.
- Maintenance and Support: Choose systems with robust warranties, easy maintenance, and strong local service networks.
- Automation and Controls: Advanced controls offer energy savings, remote monitoring, and safety diagnostics.
- Space and Installation Requirements: Consider available space, venting needs, and site access for installation or retrofits.
- Compliance and Certification: Ensure the boiler meets all local, state, and federal codes, as well as industry standards (ASME, ISO, etc.).
Choosing the Right Industrial Boiler Supplier
Partnering with the right industrial boiler manufacturer or supplier can make a significant difference in project success, long-term reliability, and total cost of ownership. Here’s how to streamline your supplier selection process:
- Compare at least 5 or 6 reputable industrial boiler suppliers or manufacturers.
- Review each supplier’s business profile, areas of expertise, and track record with similar projects.
- Request and compare detailed quotes using a standardized RFQ form to ensure apples-to-apples evaluation.
- Examine after-sales support, warranty terms, and availability of spare parts and service technicians.
- Use proprietary website previewers and online reviews to get an idea of each company’s specialization and customer satisfaction.
- Contact multiple suppliers directly with your project specifications for personalized recommendations and pricing.
Frequently Asked Questions About Industrial Boilers
- What maintenance is required for industrial boilers? Regular inspections, burner calibration, water treatment, and cleaning of heat exchange surfaces are essential for efficiency and safety.
- How can I improve the efficiency of my existing boiler system? Consider retrofits such as economizers, condensate recovery, burner upgrades, or insulation enhancements.
- What are the signs that a boiler needs to be replaced? Frequent breakdowns, high fuel bills, declining performance, or inability to meet new regulatory standards signal it’s time for an upgrade.
- How do I size a boiler for my facility? Consult with engineering experts who will assess your load profile, process needs, and future expansion plans.
- Are financing and leasing options available for industrial boilers? Many suppliers offer flexible purchasing arrangements to help manage capital expenditures.
Conclusion: Maximizing Value with the Right Industrial Boiler Solution
Industrial boilers are foundational to productivity, efficiency, and safety in countless industries. Understanding the different types of boilers—such as steam, hot water, fire tube, water tube, electric, oil, and condensing models—along with their fuel options, applications, and decision factors, empowers you to choose the right system for your operation. Whether you’re upgrading an aging boiler, expanding facility capacity, or building a new plant, working with knowledgeable suppliers and leveraging advanced boiler technology will deliver long-term reliability and cost savings.






 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services